Core Components
Dusk is built with a modular architecture, leveraging the tools and components, specifically designed to meet institutional standards for privacy, regulatory compliance, and secure interactions with regulated assets. These components enable Dusk to support not only the tokenization of real-world assets (RWAs) but also native issuance.
What sets Dusk apart from other blockchains is its tailor-made architecture, driven by continuous cryptographic research to ensure compliance, privacy, and robust network security, providing a reliable foundation to be a Decentralized Market Infrastructure (DeMI).
DuskDS
DuskDS is the settlement, consensus, and data availability layer at the foundation of the Dusk architecture. It provides finality, security, and native bridging for all execution environments built on top, including DuskEVM and DuskVM. By modularizing the protocol stack, DuskDS is built to meet institutional demands for compliance, privacy, and performance.
DuskDS includes Rusk (the node implementation) which is powered by Succinct Attestation (PoS-based consensus), Kadcast (P2P networking layer), and the Transfer and Stake Genesis contracts. Together, these elements form a secure, compliant, and composable environment for regulated financial applications
Through its dual transaction models (Phoenix and Moonlight), it provides a secure settlement and data availability layer for compliant execution environments (such as DuskEVM and DuskVM). For seamless, trustless transfers between execution layers, DuskDS exposes a native bridge.
Rusk
Rusk can be thought of as the technological heart of the Dusk protocol, similar to the motherboard of a computer. It is the reference implementation of the Dusk protocol in Rust. Rusk serves multiple critical functions. It includes foundational elements like the genesis contracts, such as the transfer and stake contract. It integrates key components such as Plonk, Kadcast and Dusk VM, and supplies host functions to smart contract developers through Dusk Core. Beyond that, Rusk houses the consensus mechanism and node software, maintaining the chain state, database and network. It also provides crucial external APIs through the Rusk Universal Event System (RUES).
Deep dive into Rusk implementation
Succinct Attestation
Succinct Attestation (SA) is DuskDS’s permissionless, committee-based proof-of-stake consensus protocol. It uses randomly selected provisioners to propose, validate, and ratify blocks, providing fast, deterministic finality suitable for financial markets.
At a high level, each round goes through three steps:
- Proposal – a provisioner creates and broadcasts a candidate block.
- Validation – a committee checks the block’s validity.
- Ratification – another committee confirms the validation outcome and finalizes the block.
For the full protocol specification and security analysis (including committee selection, finality, and slashing), see Section 3 “Consensus mechanism” of the Dusk Whitepaper (2024).
Transactions in DuskDS
Transactions in DuskDS are managed by the Transfer Contract. The Transfer Contract oversees the handling of both transparent and obfuscated transactions within the network.
The Transfer Contract supports both a UTXO and account-based model through Phoenix and Moonlight to handle transfers of the native currency, gas payments, and serve as a contract execution entry point.
Moonlight provides public transactions, while Phoenix enables shielded transactions. The flexibility of this dual-model allows users to take the best from both privacy and compliance features.
Execution environments
Dusk is designed to support multiple specialized execution environments, each optimized for distinct use cases (including FHE for confidential transactions to full EVM equivalency). These environments sit atop DuskDS and inherit its secure, compliant settlement guarantees. By separating execution from settlement, Dusk enables high-performance computation without compromising on regulatory alignment or composability.
Dusk VM
Dusk VM is a highly optimized virtual machine built around Wasmtime, a WASM runtime. It is a ZK-friendly virtual machine, enabling the development and execution of privacy-focused smart contracts and applications.
Dusk VM is fundamentally different from many blockchain VMs in that it not only executes WASM and is able to natively support ZK operations like SNARK verifications, but it also has a completely different way in which it handles memory.
Dusk EVM
Dusk EVM is a fully EVM-equivalent execution environment. Built on the OP Stack with support for EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding), it enables developers to deploy smart contracts using standard EVM tooling—while benefiting from DuskDS’s regulatory compliant infrastructure.
Network Layer: Kadcast
Kadcast is an innovative peer-to-peer protocol used by Dusk to optimize message exchanges between nodes. Unlike the traditional Gossip protocols used by many blockchain protocols, which broadcasts messages to a random set of nodes, Kadcast uses a structured overlay to direct message flow. This drastically reduces network bandwidth and makes latency much more predictable, and at the same time lower compared to Gossip protocols.
Kadcast is highly resilient to network changes and failures. It dynamically updates routing tables to handle node churn, making it suitable for decentralized environments where network conditions can be unpredictable. Even when nodes fail to forward messages, Kadcast’s built-in fault tolerance ensures alternative paths are used, maintaining reliable message delivery.
Deep dive into Kadcast implementation
Genesis Contracts
Dusk contains two fundamental Genesis contracts, which are contracts that are available when the network starts, known as the stake and transfer contracts.
The Stake Contract manages the stakes of node provisioners (stakers). It tracks active provisioners, records their rewards, and provides functions to stake, unstake, and withdraw rewards.
The Transfer Contract is responsible for the transferring of DUSK, regardless of the transaction model used.
Applications
Applications powered by Dusk provide decentralized market infrastracture (DeMI) for regulated finance. While Zedger and Hedger facilitate secure asset lifecycle management, Citadel enables self-sovereign identity (SSI) with selective disclosure. These applications are designed to meet regulatory standards without compromising on decentralization, privacy, or usability.
Zedger / Hedger
Zedger is an asset protocol that incorporates a unique hybrid transaction model combining the benefits of both UTXO and account-based transaction models. This model provides the Confidential Security Contract (XSC) functionality necessary for Dusk’s securities-related use-cases among them the full lifecycle management of securities and supporting full regulatory compliance.
Zedger allows for the digital representation, native issuance and management of securities in a privacy-preserving manner. Issuers of securities are able to issue, manage, and let investors trade securities as XSC tokens It offers built-in support for compliant settlement, redemption of securities, preventing pre-approved users from having more than one account, supports dividend distribution and voting, and can handle capped transfers. Zedger aims to support a range of security types, like stocks, bonds and ETFs. The emphasis on regulatory compliance and privacy ensures that all operations meet the highest standards required by financial authorities and stakeholders.
Differently from Zedger, which operated directly on Rusk, Hedger runs on DuskEVM leveraging the EVM equivalency of Dusk’s new execution layer. ZK operations in Hedger are handled via precompiled contracts provided by DuskEVM, mirroring the functionality once exposed through host functions in Rusk. This shift enables significantly easier developer access to privacy-preserving logic, while preserving the regulatory guarantees and auditability required for compliant finance.
Citadel
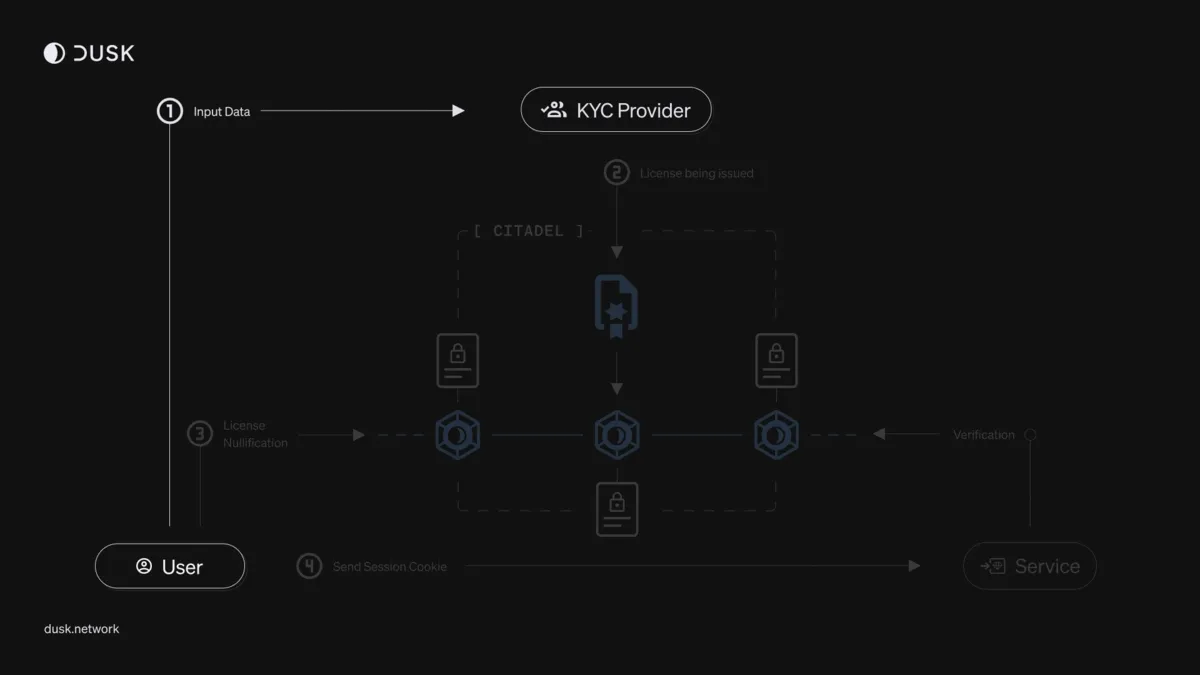
Citadel is a Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)/Digital Identity (DI) protocol designed for authenticating with third party services while upholding user privacy. With Citadel it’s possible to anonymously prove identity information, like meeting a certain age threshold or living in a certain jurisdiction, without revealing the exact information or revealing more information than is necessary. Given that Citadel is part of the network, it has wide ranging applications for on-chain activity and realizing compliance in regulated financial markets.